Remote Work Wages and the Income Distribution
Status: In Progress
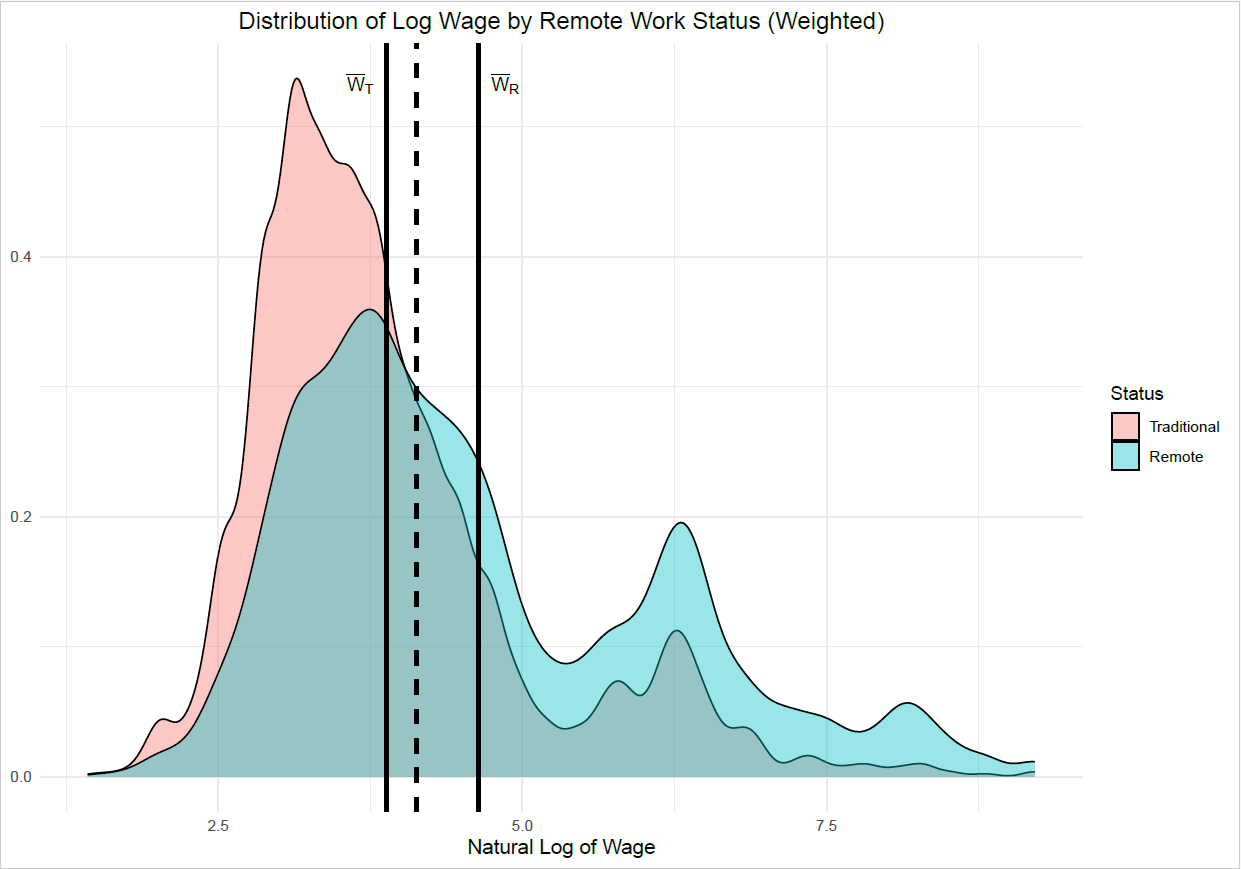
I examine the difference between remote and traditional wages. On average, remote workers are paid more than their traditional counterparts. The difference is further decomposed into two effects: A composition effect and a market return effect. The wage difference between remote and traditional workers increase along the wage distribution. In addition, this increase is dominated by increased market returns for remote work.
Remote Work and Time Allocation: Where does the time go?
Status: In Progress
Measuring Inequality of Opportunity: A Social Interactions Approach
Status: In Progress
On the Measurement of Intergenerational Mobility in Germany and the United States
Status: Draft Ready